Knee Replacement Surgery in Mumbai
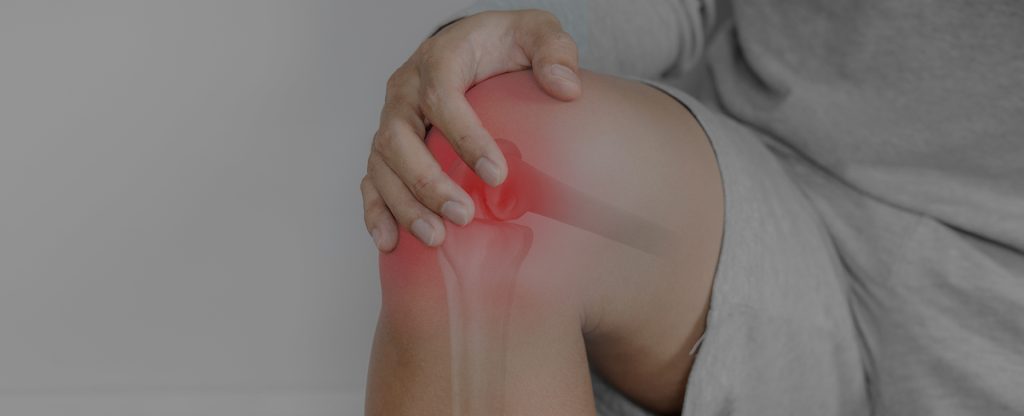
Knee Anatomy
The human knee is considered one of the most complex structures in the body. The knee consists of the lower end of the femur (thigh bone), the upper end of the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap). Several ligaments, tendons, and muscles attach to the bones of the knee joint to enable multi-directional mobility and provide stability. In addition, menisci are cartilaginous tissues present between the two articular ends of the joint. These work like a cushion between the articular surfaces, absorbing shock as they move. The knee joint is responsible for almost every movement, such as walking, running, swimming, etc.
Conditions causing knee pain
- Ligament injury- ACL tear, MCL tear, PCL tear
- Osteoarthritis
- Meniscus tear
- Fracture
- Osteoporosis
- Genu varum
- Genu valgum
- Infection
- Dislocation
- Osteomyelitis
- Osteomalacia
- Osgood-Schlatter lesion
- Patellofemoral dysfunction
- Patellar Tendonitis/Jumper's knee
- Baker's cyst/ Political cyst
- Trauma
Some of the most common knee conditions are:
Related Services
Book an Appointment
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic joint condition of the knee that is characterized by wear and tear of the cartilage. Also known as wear-and-tear arthritis or degenerative arthritis, and is quite common among old people. Osteoarthritis has several consequences, such as bone spurs, rough joint surfaces, and restricted painful knee movement.
Symptoms
- Pain in affected joints after repetitive use
- Stiffness after long periods of inactivity
- Joint aching and soreness
- Decreased range of motion
- Grating sensation
- Loss of flexibility
Causes and risk factors
- Aging- Typically, Osteoarthritis is prevalent in individuals who are above 50 years of age.
- Gender- Women are at high risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Injuries- A history of trauma or past injuries such as ligament injuries, torn cartilage, or dislocated joints often lead to OA.
- Genetics- Having family with this condition, especially your parents, increases your risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Medical conditions- Certain metabolic diseases such as diabetes, hemochromatosis, and bone deformities also cause osteoarthritis.
- Obesity- People who are overweight are associated with a higher risk of developing OA.
Treatments
Medications
Medications are taken orally, applied topically, injected, or inserted into the body to decrease the knee pain and swelling. The most common pain relievers include acetaminophen (paracetamol) and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and diclofenac. They should be used only after being prescribed by a doctor.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is a treatment approach to help the patients obtain and maintain their highest level of function and freedom in daily life activities. It can involve activities like exercise, swimming, lifestyle modifications, and some relaxation techniques. Physical therapists can also help prevent or reduce the risk of future injuries.
Intra-articular (IA) injections
The injections that are given intraarticularly- are inserted in the space between the joints to relieve pain and swelling in the affected area. The injection procedure is painless and performed by an Orthopedic surgeon in OPD. These Injections are frequently used to treat acute and chronic osteoarthritis flare.
Intra-articular injections decrease acute episodes of pain and increase joint mobility.
IA injections of corticosteroid and hyaluronic acid are safe and have positive effects on patients.
Corticosteroids have both anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, hence decreasing the erythema, swelling, heat, and tenderness of the inflamed joints. HA helps to restore normal viscoelastic properties, reduction of synovial inflammation, protection against cartilage erosion, and promotion of HA production.
Surgery
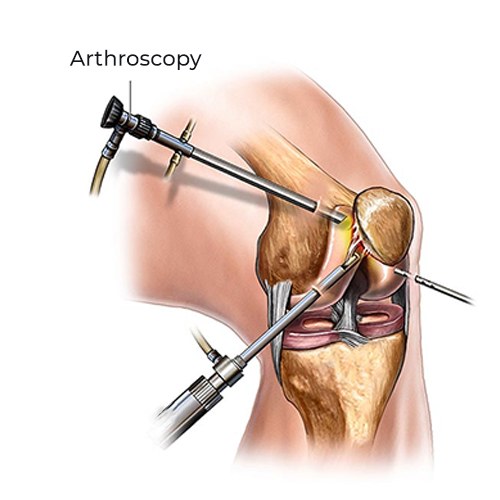
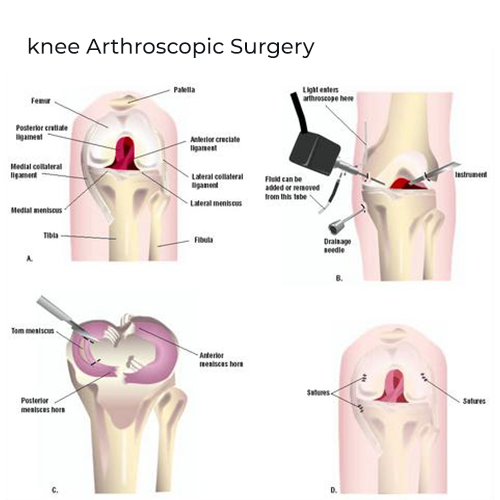
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopic knee surgery is a safe procedure that is performed using an arthroscope, a viewing instrument, to consider the knee joint to diagnose knee problems.
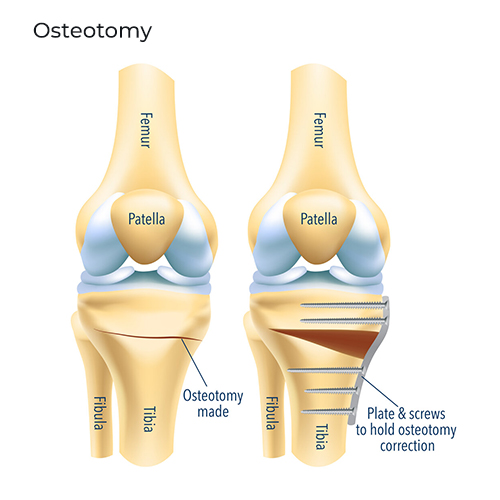
Osteotomy
Knee Osteotomy is mostly recommended to reduce osteoarthritis joint pain in younger, active patients. It is performed to correct the alignment of the bones of the knee joint.

Partial & Total
Total knee replacement surgery-Total Knee Replacement Surgery involves replacing both the articular parts of the knee joint with a prosthesis. Partial knee replacement surgery-Partial knee replacement surgery involves replacing the only damaged (medial)parts of the knee with prosthetic components.
Who is a candidate for total knee replacement surgery?
You are a candidate for total knee replacement if:
- Your quality of life is severely affected
- You suffer daily pain
- Your day-to-day activities are restricted
- You have evidence of significant radiographic changes in your knee joint


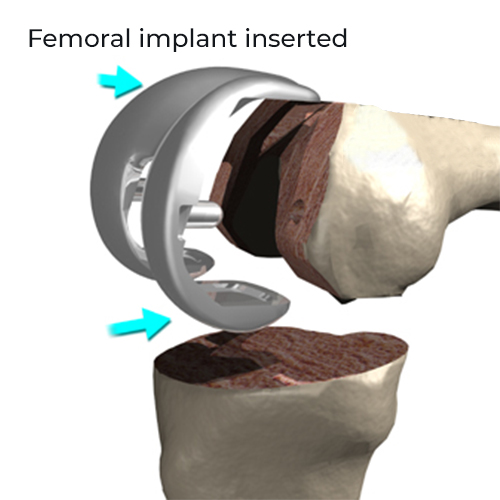
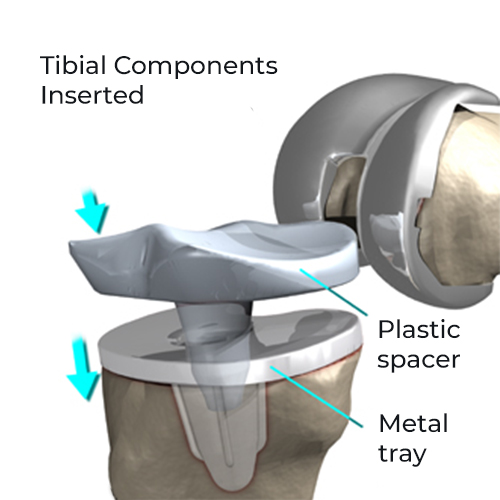
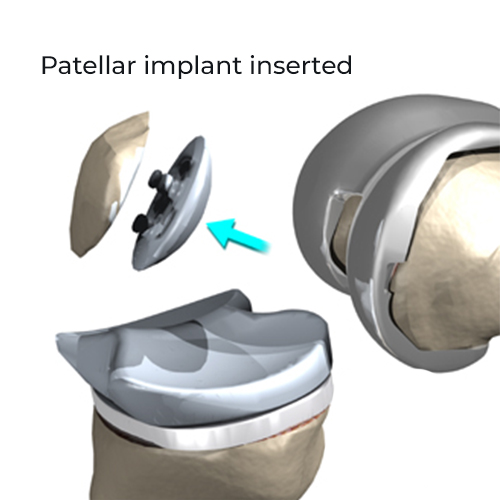
Post Operative Rehabilitation
Post Operative Rehabilitation
- Rapid post-operative mobilization and exercises to increase the range of motion.
- Incorporation of a motorized CPM (continuous passive motion) device to reduce joint stiffness and improve range of motion by passively moving the joint.
- Passive extension by placing a pillow under the foot to allow some relaxation to the knee.
- Muscle-strengthening exercises to build strong and healthier knee muscles to prevent injuries in future.
- Inclusion of weight-bearing on the first post-op day itself to improve knee strength.
Surgery is the last resort treatment for osteoarthritis and is performed only when the condition can’t be cured with medicines and therapies. The most common surgery performed to correct osteoarthritis is Total Knee Replacement Surgery. It involves replacing both the articular parts of the diseased knee joint with a prosthesis. This surgery is very effective for restoring functions in the knee area affected with arthritis and provides relief from pain.
Ligament Injury
The knee is mainly stabilized by four ligaments- the connective tissues present in between the bones and joints. Knee ligaments can get torn or injured due to excessive stretching or a twisting motion. A ligament injury makes the knee unstable and causes severe pain. The knee comprises cruciate and collateral ligaments:
Cruciate Ligaments
ACL Ligament
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) resists anterior translation. ACL is one of the key ligaments that stabilize the knee joint and it controls the rotation and forward movement of the shin bone. The ACL injury is most common and it results in limited knee movement and causes stiffness, swelling, and extreme pain.
The risk factors for ACL injury are as follows:
- Stress on the knee during sports and fitness activities
- Very hard blow on side of the knee
- Trauma or fall
- Slowing down suddenly or landing on an awkward jump
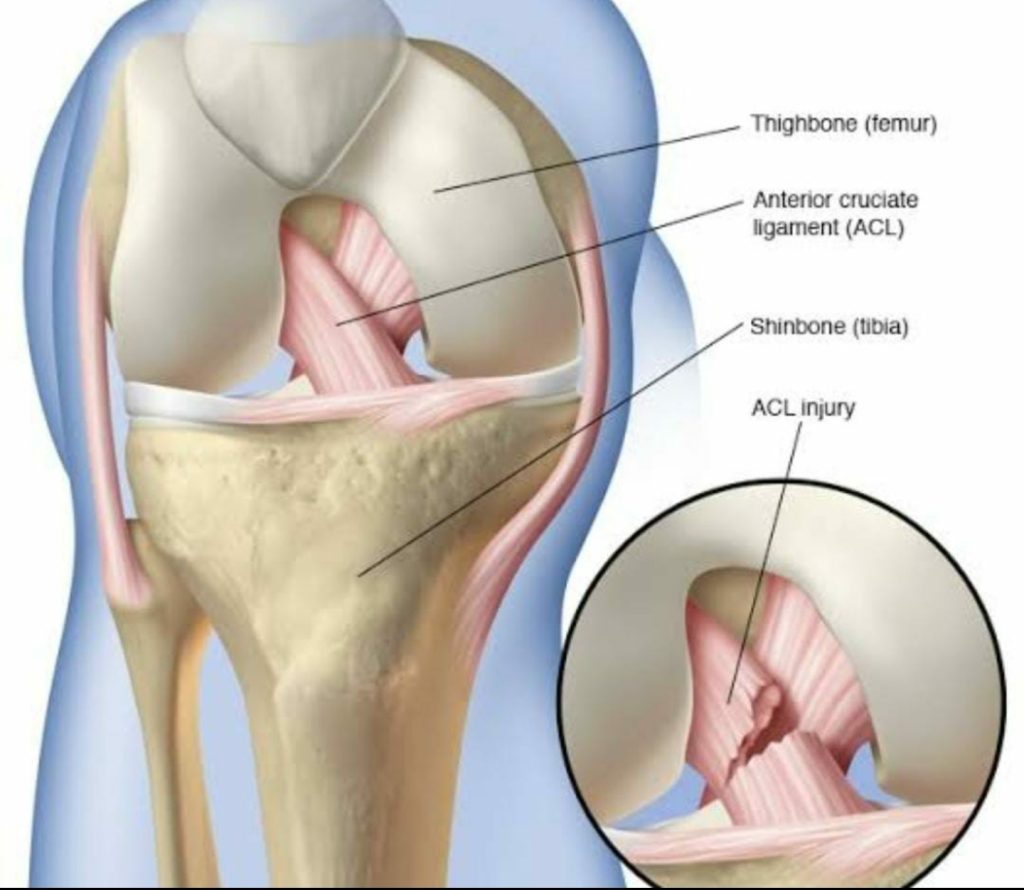
PCL Ligament
PCL (posterior cruciate ligament) controls the backward movement of the knee and resists posterior translation.
Collateral Ligaments
MCL Ligament
MCL (medial collateral ligament) stabilizes the knee by giving support to the inner knee and resists medially directed force.
LCL Ligament
LCL (lateral collateral ligament) provides the necessary support to the outer knee and resists laterally directed force.
Symptoms
- Rapid swelling within 24 hours
- Loss of full range of motion
- Tenderness along the joint
- Discomfort while walking
- When ACL is injured, there might be a popping sound
Causes
- Blow to the knee- A hit or blow to the outer side of the knee while playing sports can cause injury in the medial collateral ligaments of the knee (MCL).
- A sudden twist of the knee- Sudden twisting motion which involves the feet staying planted one way, but the knees turning the other way can cause injury in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
- Incorrect stretching- Incorrect stretching during workouts often causes ligament injuries.
Treatments
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen help with pain and swelling. While taking the medicines, it is important to follow the directions exactly prescribed by the doctor. Your doctor may also recommend wearing a knee brace to stabilize the knee and protect it from further injury.
Exercises
Practicing muscle strengthening and stretching exercises recommended by the doctor helps you recover from the ligament tear symptoms.
Surgery
If the symptoms do not respond to conventional treatment, an ACL Reconstruction Surgery is recommended to repair the damaged ligament.
ACL Reconstruction Surgery
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) surgery is recommended to treat a torn ACL ligament. It is an arthroscopic procedure in which the ACL is constructed by taking tissue grafts from the patient’s own quadriceps, hamstrings, patellar tendon, or from a donor (allograft). It uses minimally-invasive techniques to minimize damage to adjacent tissues and reduce recovery time.
Given below are the factors that are considered before the surgery:
- Degree of ACL injury
- Presence of associated ligamentous, chondral, and meniscal conditions
- Age/activity level/occupation
- Sports participation
- Patient compliance with post-op rehabilitation
Patellar Tendinopathy (Jumper's knee)
Patellar tendinopathy, also known as Jumper’s knee, refers to an injury in the patellar tendon-a cord-like tissue that joins the patella to the tibia. This condition is characterized by localized pain at the inferior pole of the tendon.
Symptoms
- Tenderness in the tendon at the front of the knee
- Pain that is aggravated by loading
- Stiffness and weakness around the knee
Causes
- Repetitive loading- Young athletes who participate in sports such as basketball and volleyball are most prone to this condition. This is because these sports and athletic activities demand repetitive loading of the patellar tendon.
- Trauma- A direct blow below the kneecap (patella) during falls or sports often leads to a jumper's knee. Repetitive stress, such as frequent jumping on hard surfaces on the patellar tendon, can also cause patellar tendinopathy.
- Sudden movements- Sudden jumping movements during running, skipping, or climbing may lead to an inflammation in the patellar tendon.
Treatment
RICE therapy
RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This is the first-line treatment needed to subdue pain and inflammation due to patellar tendonitis.
Braces and crutches
The braces and crutches are incorporated in the initial phases of knee rehabilitation to support the knee. Therefore, if your doctor has prescribed braces or crutches, do wear them even if you can walk without them, as they will prevent and redistribute excess pressure on your lower legs.
Surgical Knee Tendon Repair Through Arthroscopy
Surgery is required in stage 4 patellar tendonitis when the patellar tendon has torn and can’t be repaired with conventional treatment techniques. Arthroscopy is used to do this repair while trying to preserve the natural biomechanics of the knees. Therefore it is also called knee preservation surgery.
Prepatellar (kneecap) bursitis
Prepatellar bursitis is a condition that refers to the inflammation or irritation of the bursa in front of the kneecap. Bursa is the jelly-like substance present between the tissues and bones and reduces friction while acting like cushions. Though any of the bursa in your knee can become inflamed, knee bursitis most prevalently occurs over the kneecap or the prepatellar region.
Symptoms
- Bruising & swelling in the front knee
- Inability to bend or straighten the knee
- Soreness and pinkishness around the swollen area
- Limited range of motion
- Fever and chills
Causes
- Pressure from constant kneeling- Employees such as plumbers, gardeners, and coal miners who have to work constantly in a kneeling position are more prone to prepatellar bursitis.
- Direct blows- A direct blow to the front knee in sports or falls can also lead to this condition.
- Bacterial infection- If you have got a knee injury, a scratch, or an insect bite, your prepatellar bursa sac can get infected and may develop bursitis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis- People suffering from rheumatoid arthritis or gout are also more susceptible to kneecap bursitis.
Treatment
Activity modification
Avoid activities that worsen the symptoms and wear knee pads to prevent too much pressure on your knee. Also, pursue low-impact exercises such as cycling or using an elliptical machine.
Medications
Typically, NSAID medications are recommended for managing the pain. Our doctors can also suggest a variety of injection therapies.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the damaged bursa is required in case of severe prepatellar bursitis when the infection does not respond to the medication alone. The chronic swelling subsides after the surgery, and normal functioning of the knee is restored within a week.
Knee Replacement Surgery with Robotic Technique
A robotic knee replacement is similar to a traditional knee replacement, except for the fact that the former is done with assistance from a robotic arm or handheld robotic device. Like traditional joint replacement operation, the robotic technique is also done for osteoarthritis or injuries, where the damaged tissue or bone is removed, and a smooth artificial implant is placed.
It should also be noted that while the technology makes patients imagine that a machine takes over a doctor’s job, that’s not exactly the case. The human surgeon stays in control of the robot through the whole process.
The advantages of Robot-assisted joint replacement are as follows;
High Degree of Accuracy
The system uses advanced 3D modelling to map the anatomy of your knee and create a detailed individual plan for your operation. It enables the surgeon to pre-plan the exact cuts before operation and tailor them precisely as per your joint.
High Level of Precision
The robotic arm operates within a fraction of a millimetre. The software provides a visual path for the surgeon as the plan cuts and fixes the implant, preventing the surgeon from moving outside the planned boundaries.
Preserve the healthy bone
Another benefit of robot-assisted surgery is that it helps preserve the maximum healthy bone & tissue to reduce non-operative pain & speed of recovery.
In conclusion, it can be said that robot-assisted surgery has high accuracy, predictability, and a tailored approach for the best joint replacement. Dr. Ganesh Rajeshwar has performed many successful knee surgeries with robotic techniques.
Knee conditions are common and can happen to anyone. See your doctor immediately if you are suffering from knee discomfort and pain. You can book an appointment with Dr. Ganesh Rajeshwar- the best knee pain specialist in Mumbai. As medical science keeps advancing, so does our technology at Mumbai Ortho & Eye Clinic. We keep updating to serve you the best treatment.

